All About Cellulitis – Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
All about cellulitis – Causes, symptoms, and treatment
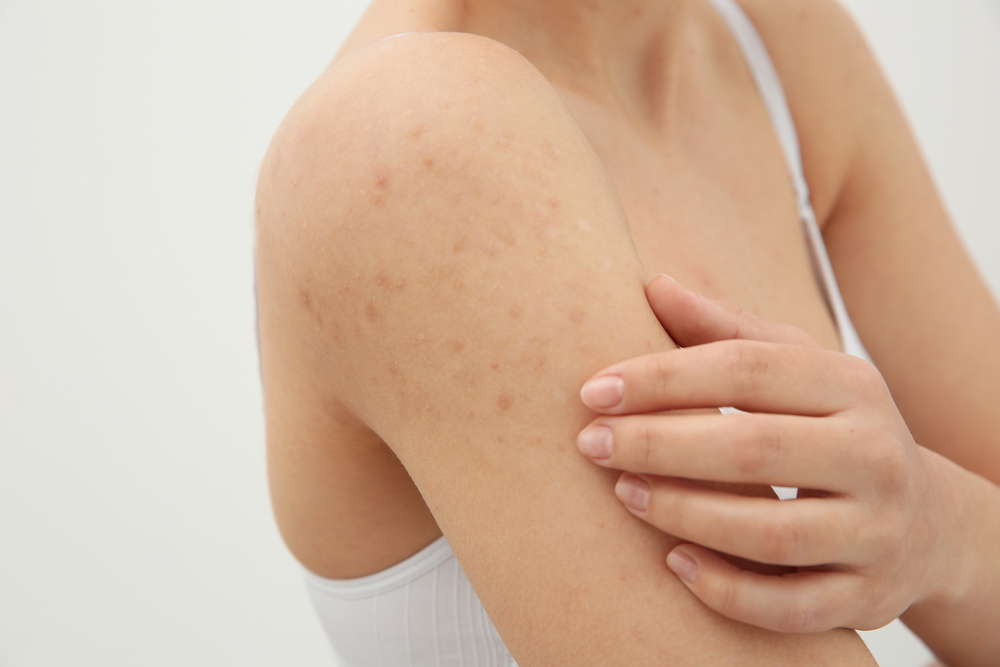
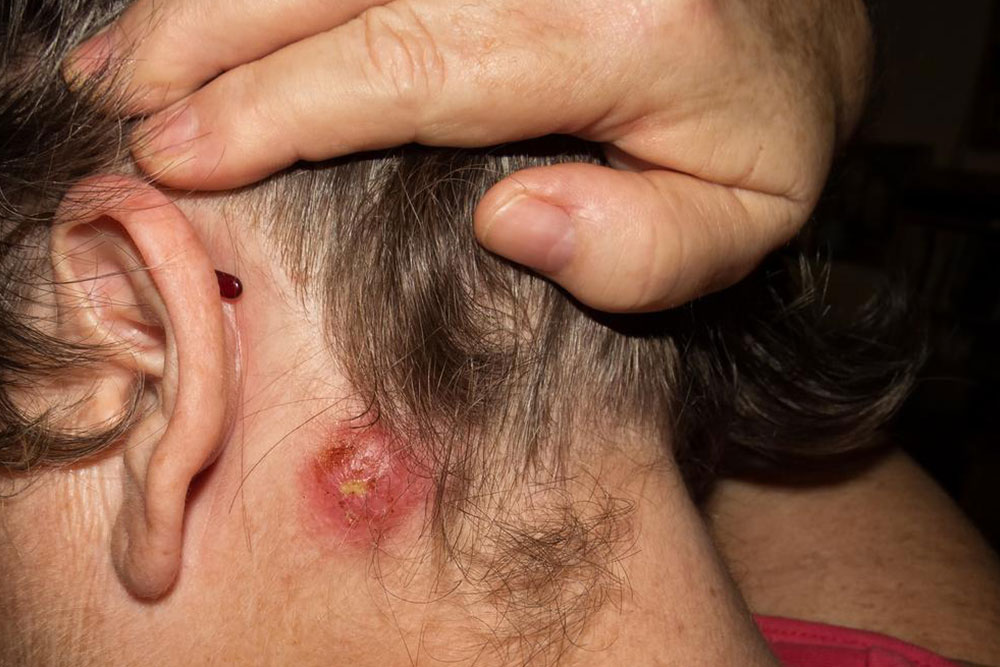
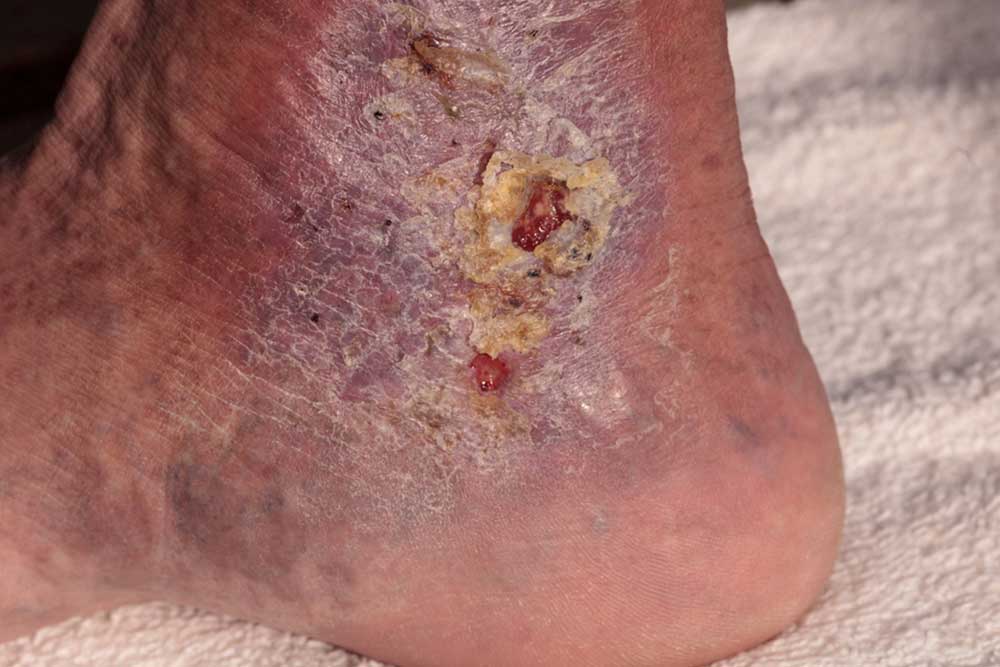
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that harms the deeper layer of the skin. This condition can become serious if left untreated. Cellulitis causes the skin to swell. The affected area also turns red and is painful to touch.
Cellulitis can affect any part of the body, including the face and neck. In adults, the most common occurrence is seen in the lower legs.
In this article, we will throw some light on the symptoms, treatment, and complications of this disease.
What are the symptoms of this disease?
- The skin turns red and, with time, the redness starts expanding and spreading.
- The affected area swells.
- It becomes tender, and you experience a sharp pain when the area is touched.
- The affected area is warm.
- In some cases, cellulitis also causes fever.
- Your skin gets covered in red spots and/or blisters.
- Skin dimpling
When should you see a doctor?
- If you have a fever along with other symptoms.
- A rash on your body, which is red, swollen, and warm.
- If the rash is expanding rapidly, a doctor should be consulted.
What are the causes of cellulitis?
- The major cause of cellulitis is the bacteria, most commonly streptococcus and staphylococcus.
- It happens when bacteria enters your system through a crack or break in the skin.
- Recently, there have been more incidences of a relatively more serious kind of cellulitis called methicillin-resistant Staphyloccocus aureus (MRSA).
- One of the causes for cellulitis could be animal bites that break open the skin, allowing the bacteria to enter.
- Old people usually have dry, flaky skin. Therefore, they are more susceptible to this infection.
Which factors put you at a higher risk of cellulitis?
- Any kind of injury, cut, fracture, or burn can give the bacteria an opportunity to enter, become one of the causes of cellulitis.
- If one suffers from leukemia, HIV, diabetes, or diseases that weaken the immune system, they are more susceptible to infections. A weak immune system could also be a result of certain medications.
- Certain skin conditions like eczema and athlete’s foot cause the skin to break and can increase the probability of cellulitis.
- If one has suffered from cellulitis in the past, the chances of them contracting it again in the future increase.
- Obesity also increases the risk of cellulitis.
What are the ways to prevent cellulitis?
- If you have an injury on your skin, wash it daily with soap and water. Do not be harsh on it. Wash it gently while taking bath to prevent bacteria from entering and spreading.
- An over-the-counter ointment such as Vaseline or Polysporin can go a long way in providing protection to your wound. Apply it every day on your surface wounds.
- In case you experience redness, pain, and/or swelling in any area of your body, seek immediate medical care.
- Check your feet daily for any signs of injury or infection.
- Moisturize your skin regularly to prevent dry skin and treat any dry skin that can lead to cracking and peeling.
- While trimming your finger and toenails, ensure that you do not cut the surrounding skin.
- Always wear covered footwear and gloves to protect your hands and feet.
- In case you are affected by a superficial skin infection, do not wait for it to heal by itself; take appropriate medical care to treat such infections.
With proper care and medical attention, cellulitis causes can be prevented as well as cured.