Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Psoriasis
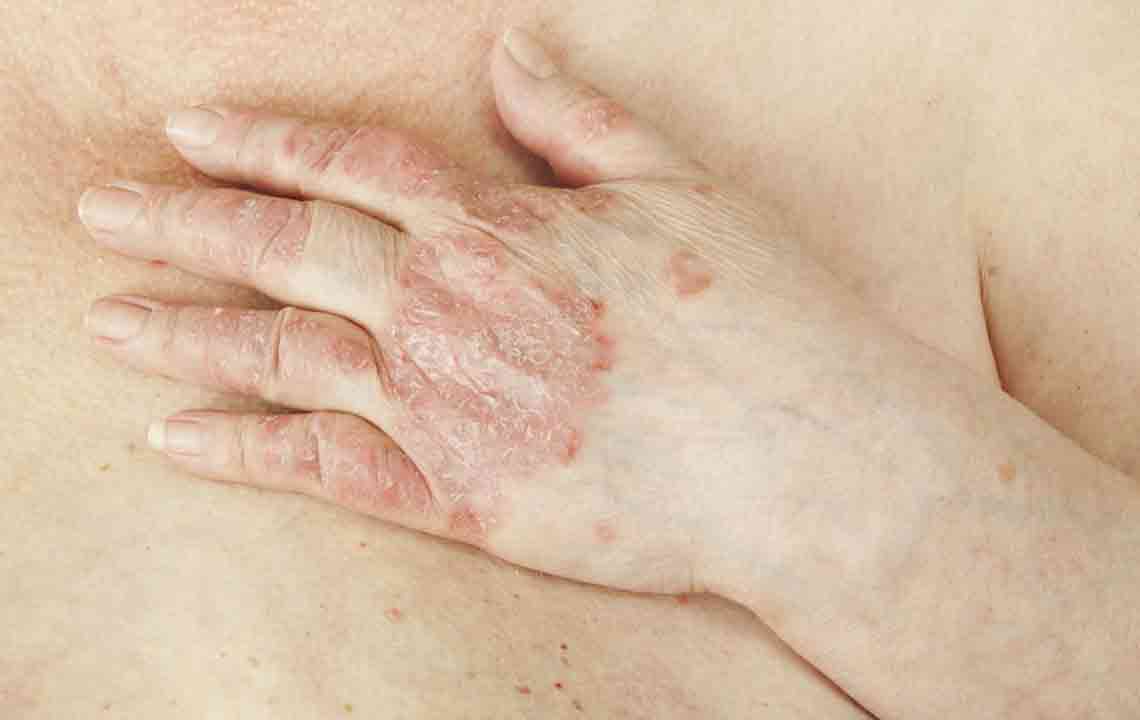
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that can happen when a problem occurs within the immune system. It is a common chronic disease that causes red, dry, scaly patches and flakes to appear on the skin. The rash often goes away with time but can flare up again after a while as a result of a trigger, such as stress.
Causes of psoriasis
Our immune system involves a type of cells called T cells.

About 3 percent of people are affected by psoriasis globally and 7.5 million in the country itself. It affects both men and women equally and can begin at any age, but is most common between the ages of 15 and 35 years, and again between 50 and 60 years.
Symptoms of psoriasis
In the case of psoriasis, instead of skin cells shedding, both dead and live cells, collect on the skin’s surface as the replacement process is fast. There are several forms of psoriasis, but these are some of the common symptoms that one can spot on people affected by psoriasis.
Main symptoms:
- Red, flaky, crusty patches overlaid with silvery scales that cast easily.
- Intense itching and burning sensations.
Symptoms differing according to the types:
The severity of psoriasis can fluctuate from mild to severe. According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, the symptoms can be as follows:
- For a person with mild psoriasis, it covers less than 3 percent of the body.
- For a person with moderate psoriasis, it can affect between 3 to 10 percent of the body.
- For a person with severe psoriasis, it covers over 10 percent of the body.
Around 80 percent of people suffer from mild psoriasis and the other 20 percent may either have moderate or severe psoriasis. It can appear in any part of the body but is mostly spotted as small patches on the elbows, knees, lower back, and scalp.
Treatments
A person who suffers from persistent rashes that do not go away with over-the-counter (OTC) treatment should consider asking the doctor about it. If a diagnosis for psoriasis is confirmed, the treatment depends on the type and the severity of the condition. The main treatments include topical treatment, systemic therapy, and phototherapy.
- Topical treatment
Topical treatment for psoriasis is directly applied to the skin. This is usually the first line of treatment with an aim to slow down the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation. The treatments are available on prescription and include non-steroids and steroids. - Systemic therapies
Systemic therapies for psoriasis work for the entire body. This therapy is used for people with moderate to severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. These can be either taken orally or by injection and include acitretin, cyclosporine, and methotrexate. Biologic drugs, a protein-based drug made from living cells, are a type of systemic therapy that target specific T cells that are associated with psoriasis. - Phototherapy
Phototherapy is a light therapy where the skin is exposed regularly to ultraviolet light either at the doctor’s or at home and is done under medical supervision.