Common Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
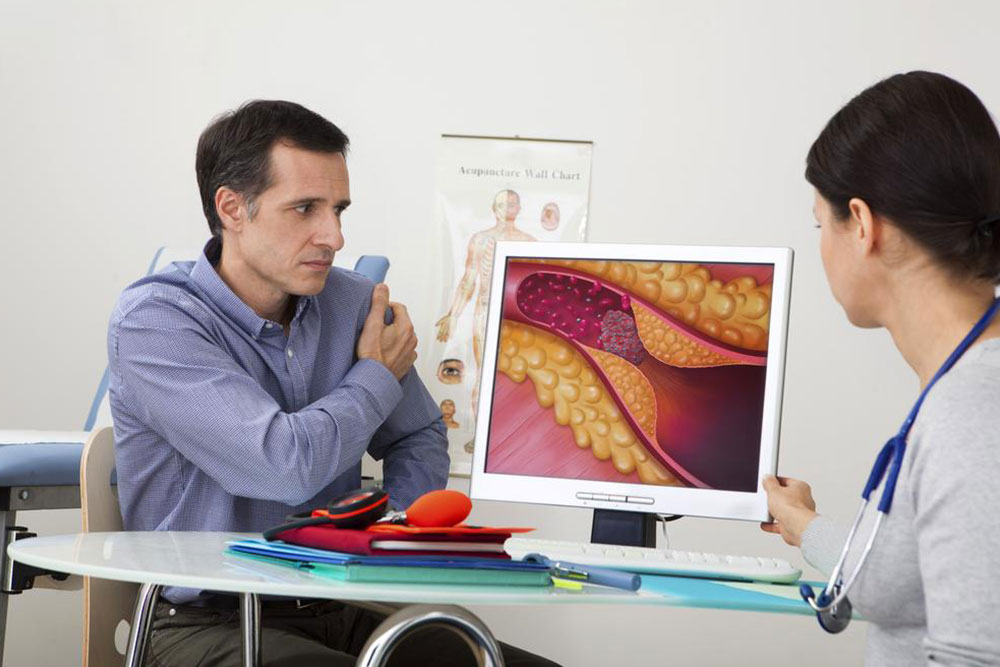
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a critical condition that occurs due to the formation of a blood clot in a vein that is located deep inside your body. Deep vein thrombosis often occurs in your thigh or lower part of the leg. Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis in the leg are often mistaken for symptoms of other health conditions.
A blood clot is a solid, gelatinous deposit of coagulated blood.
Who is at a risk of DVT?
The risk factors for developing deep vein thrombosis are as follows:
- Sitting or standing for long periods of time
- Injuries
- A catheter placed in veins
- Obesity
- A family history of DVT
- Smoking and alcoholism
- Hormone therapy
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis
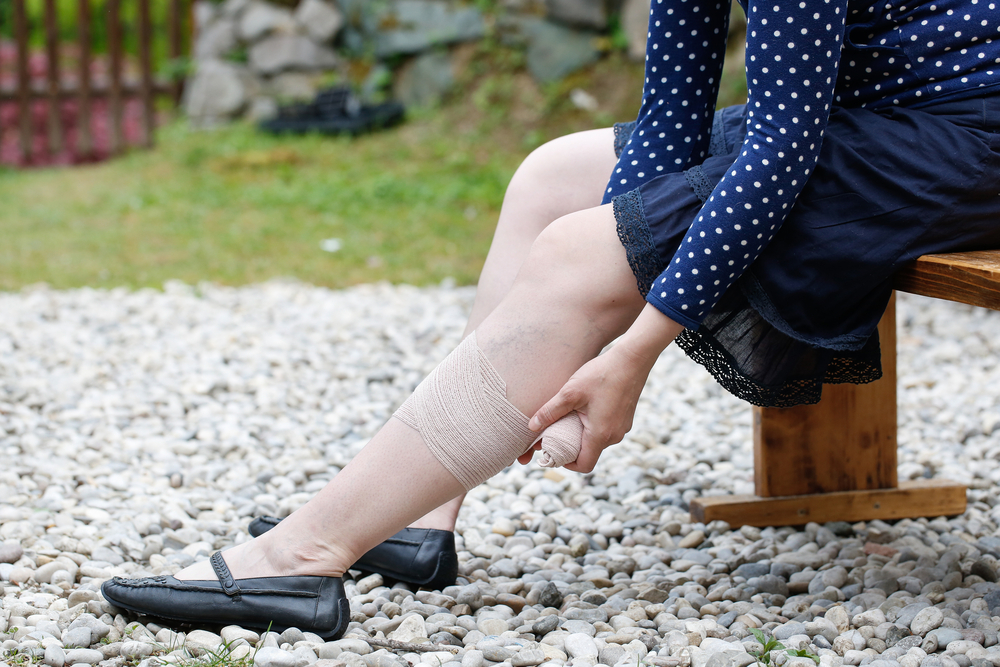
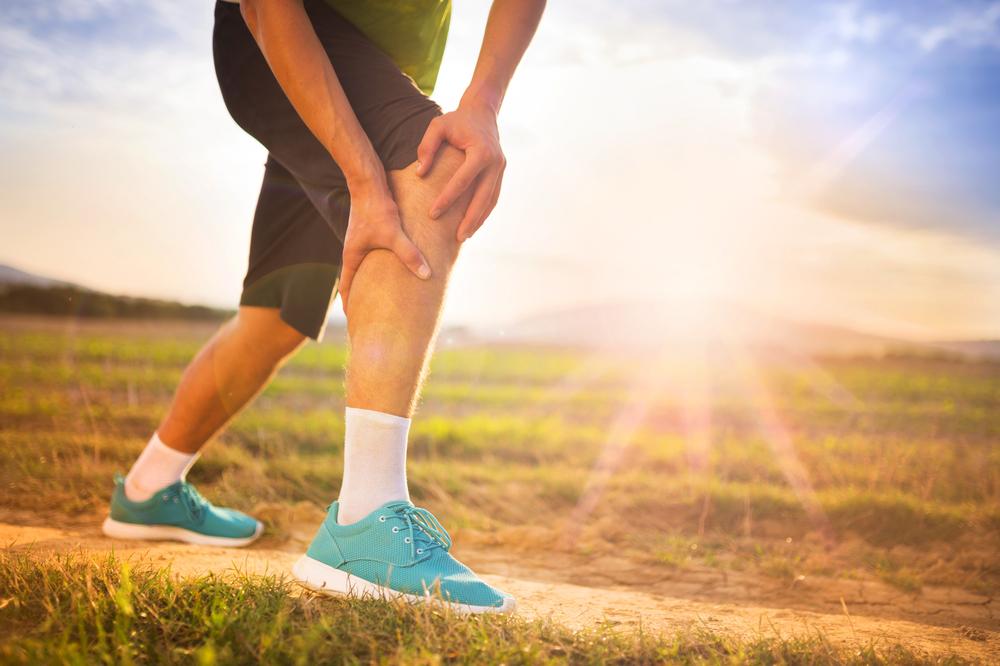
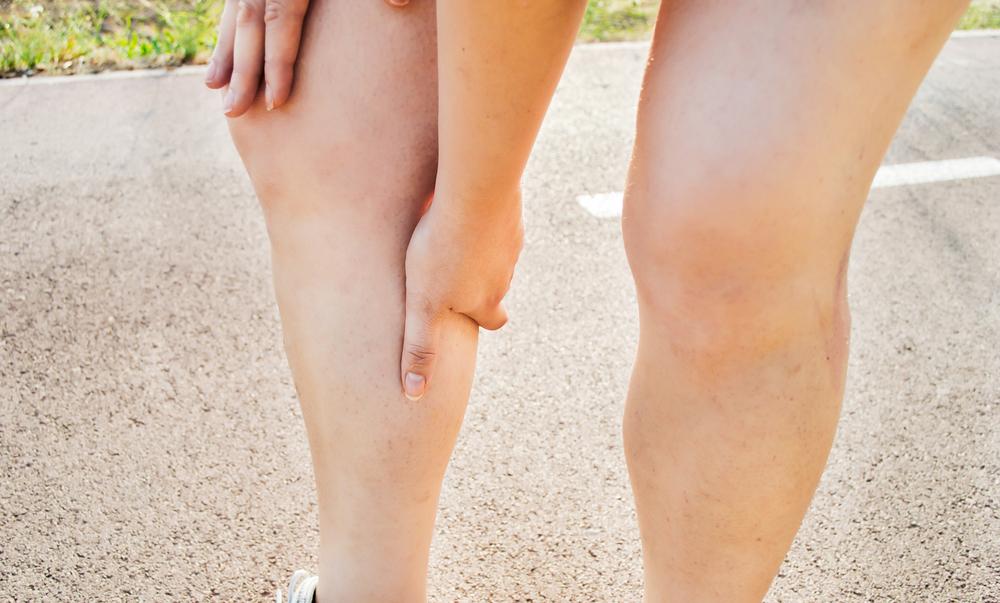
Thighs or lower part of the leg are common areas for deep vein thrombosis. Available DVT pictures show swollen, red or discolored legs of individuals affected by the condition. However, some people affected by the condition do not show any symptoms of deep vein thrombosis in the leg. Symptoms of DVT that occur suddenly are a cause of concern and require immediate medical help. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling in one or both legs
- Severe pain and tenderness upon standing or walking for long periods
- Warm leg skin
- Swollen, reddish or hard veins in legs
- A reddish or discolored skin on legs
A complication of deep vein thrombosis is known as pulmonary embolism. This is a life-threatening condition that requires emergency medical help. Symptoms associated with pulmonary embolism are as follows:
- Sudden, severe cough that brings up blood
- Sudden sharp chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty breathing or painful breathing
- Rapid heartbeat
- Light-headedness
Deep vein thrombosis typically occurs in individuals above the age of 50 years. Deep vein thrombosis is also referred to as the post-thrombotic syndrome, thromboembolism, and post-phlebitic syndrome. Those above the age of 60 years and/or smokers are at a higher risk of DVT, and therefore, they need to be vigilant of the symptoms. Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis of the leg worsen when the thrombosis travels to the lungs, thereby causing pulmonary embolism