How often should you check your sugar levels?
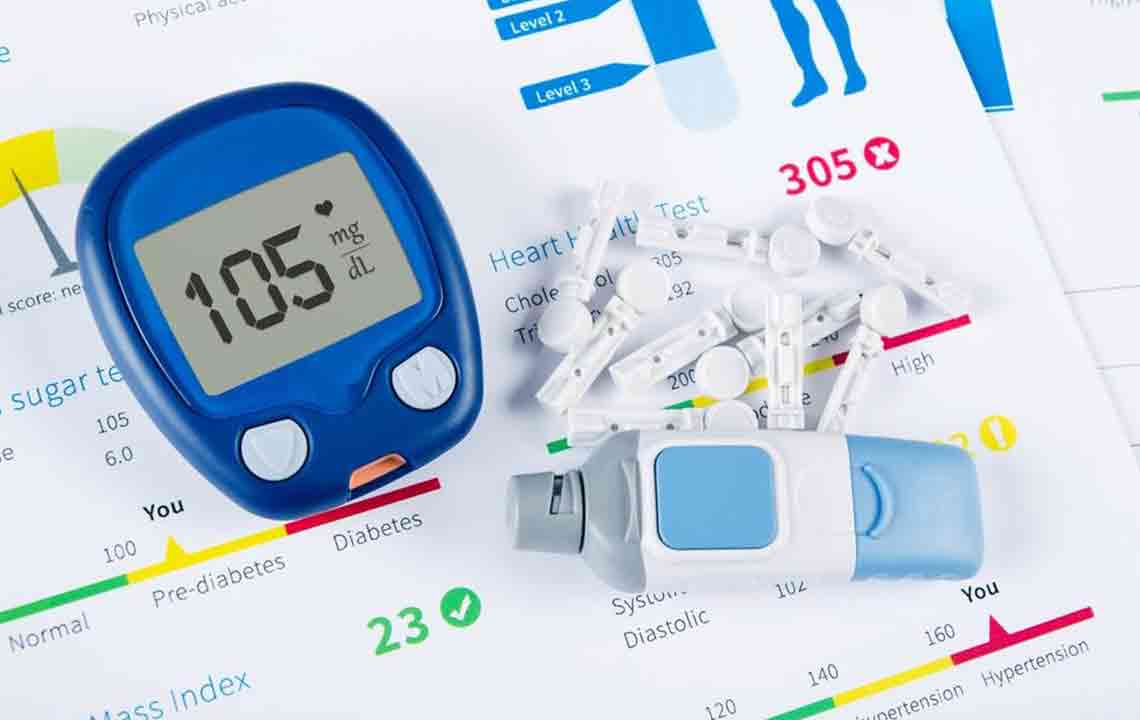
Diabetes is a growing problem, and every doctor suggests that diabetic patients should keep a regular check on their blood sugar levels if they want to keep their diabetes under control. For this purpose, diabetes tests are very important. With technology advancing so fast, keeping a check on sugar levels has become easier than before because of electronic devices that are available in the market.
When should you conduct a test to check the levels of your blood sugar?
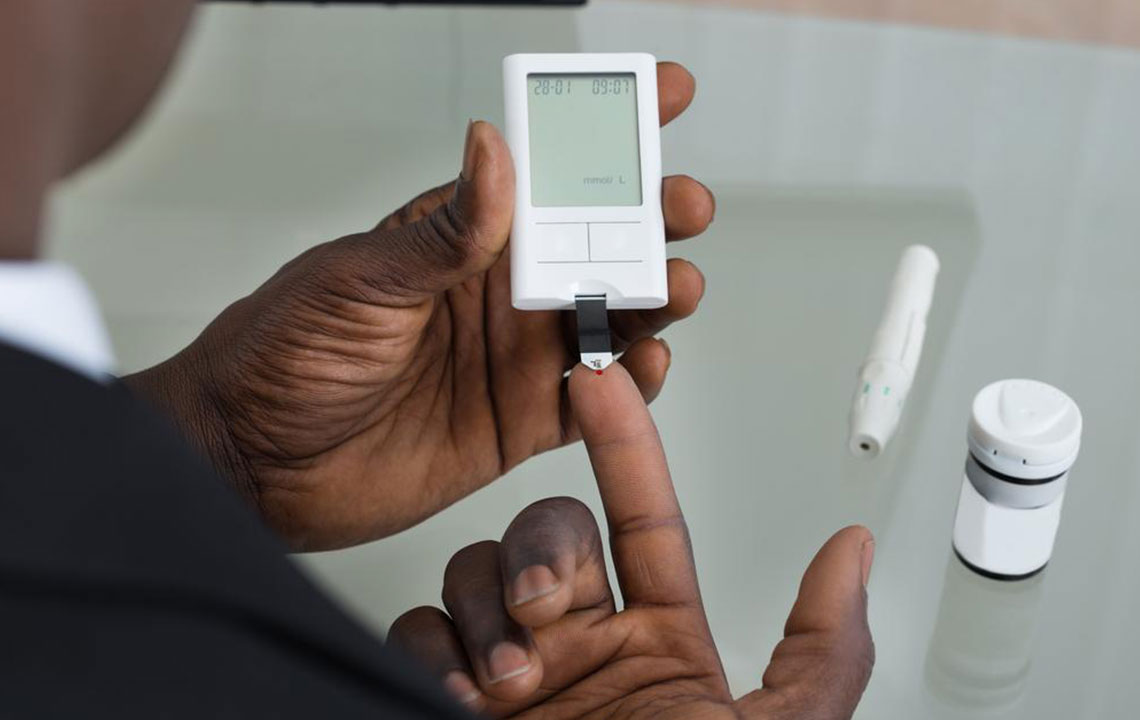
Blood glucose should be frequently checked. But how often? Well, the answer to this depends on the type of diabetes that you are suffering from.
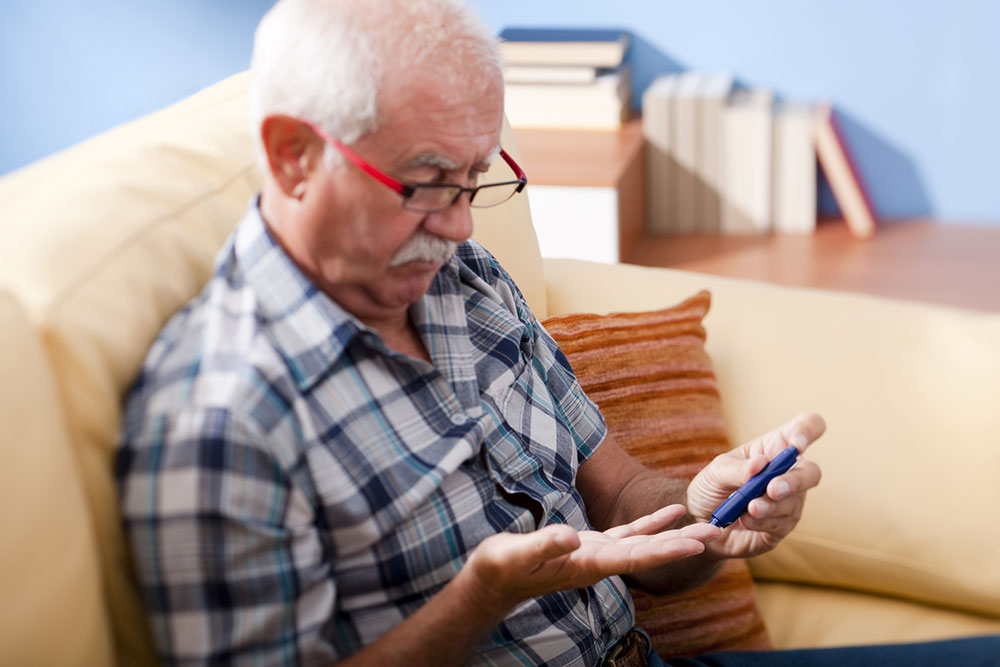
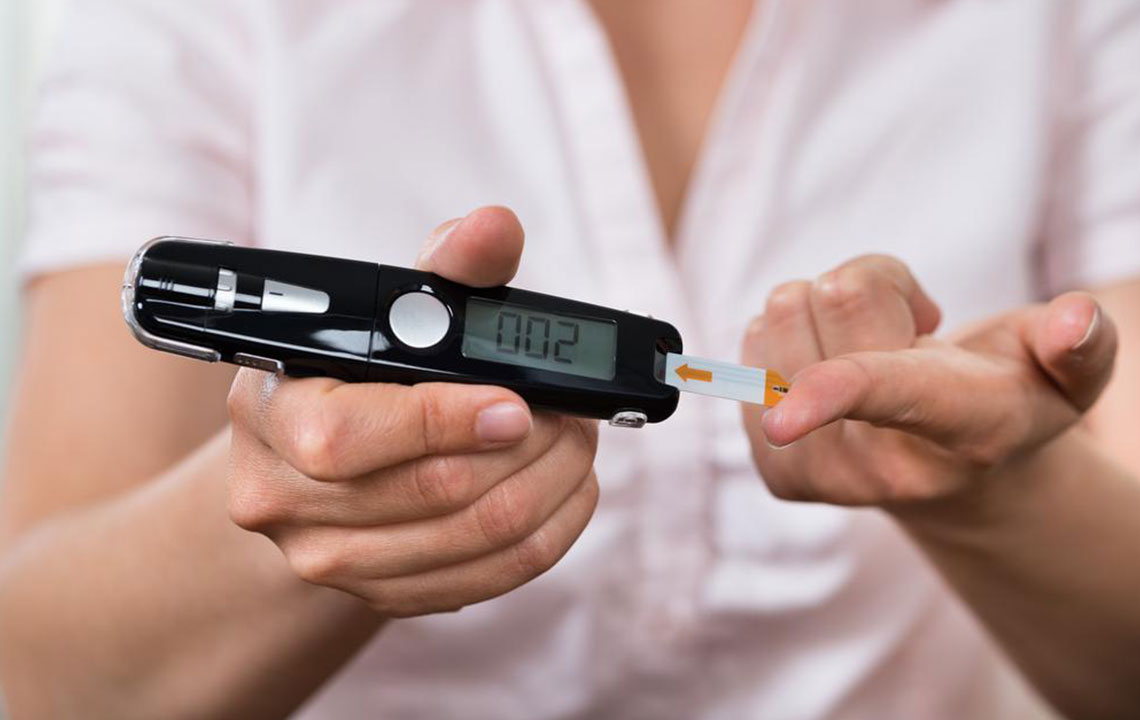
- If the patient has type 1 diabetes, then the doctor usually advises the patient to test their blood sugar at least five to seven times a day. The doctor will direct the exact time of testing. Most doctors advise testing before and after meals, before and after exercise and other day-to-day activities to check the effect of these activities the blood sugar level. Self-diabetes tests come to the rescue when you have to test glucose levels many times daily.
- Patients who are administered insulin for treating their type 2 diabetes are usually advised by the doctors to undertake diabetes tests at least twice a day or even more depending upon several other factors. The time of testing is usually similar to type 1 diabetes, that is, before and after meals and sometimes even before going to bed. But sometimes patients can keep their type 2 diabetes under control without the use of insulin-based medications. For such patients, frequent checking of blood sugar is not always required.
- Apart from these two types, the frequency of testing blood sugar also depends on the severity of the condition and the age of the patient.
- For women who have gestational diabetes, diabetes tests follow a different pattern and usually vary from patient to patient although checking the blood sugar levels before and after meals is something that remains common to all form of diabetes.
Disclaimer:
The content of the articles discussing symptoms, treatments, health conditions, and side effects is solely intended for informational purposes. It is imperative that readers do not interpret the information provided on the website as professional advice. Readers are requested to use their discretion and refrain from treating the suggestions or opinions provided by the writers and editors as medical advice. It is important to seek the help of licensed and expert healthcare professionals when necessary.