How to Inject and Use Insulin: A Diabetic’s Guide
Insulin is a common term in households with a diabetic patient. The injection and use of insulin is important part of a diabetic’s daily life. While insulin is mainly used by those with type 1 diabetes, it is often necessary for those with type 2 diabetes as well.
There are many different insulin routines that a doctor may suggest. Since diabetes is a highly individualized disease, with symptoms and reactions differing from person to person, there are a variety of insulin therapy plans available.
Insulin Use for Type 1 Diabetes
Those with type 1 diabetes are usually put on a traditional syringe plan. The patient can inject insulin twice per day, gradually increasing the amount to three or four injections per day depending on the insulin type and need. Since each individual’s blood glucose levels are different, there are many different types of insulin available to assist with the maintaining of those glucose levels. With the frequent injection of insulin, those with type 1 diabetes can prevent stroke, nerve damage, kidney failure, and more.
Insulin Use for Type 2 Diabetes
Individuals with type 2 diabetes do often require insulin, but not as frequently as those with type 1 diabetes. Some patients need a single injection of insulin before bed, along with the usual intake of diabetes pills with oral medications and lifestyle changes are not enough. If the pills were to stop working then more injections of insulin would be needed.
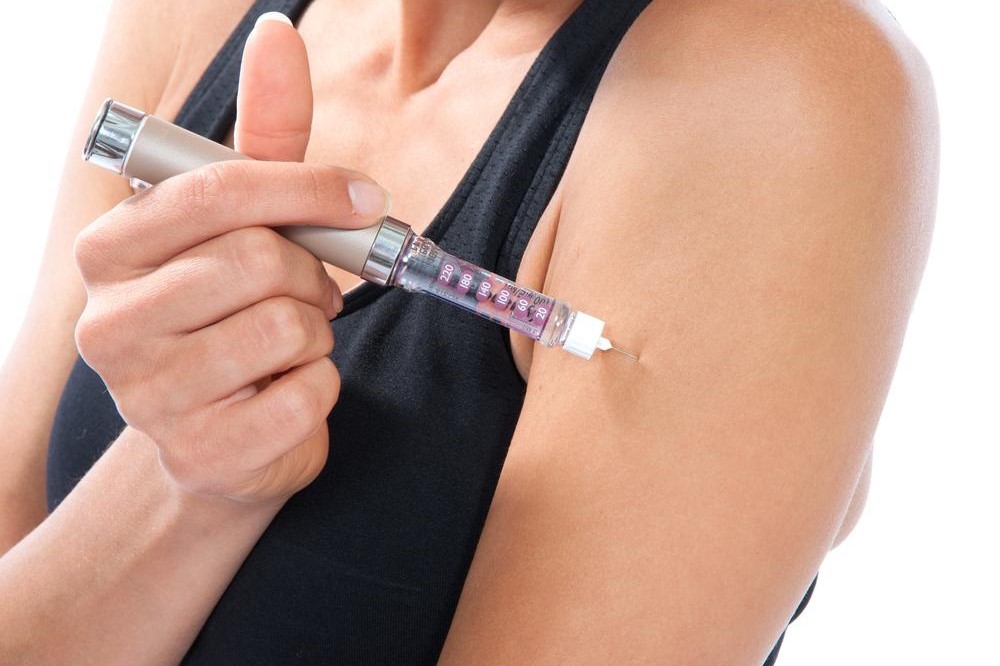
Different Ways to Take Insulin
People usually refer to insulin intake as injections, but it doesn’t always have to be done with a needle and syringe. If you are afraid of needles, or uncomfortable with traditional injections, there are many ways in which insulin can be ingested. The most popular ways to take or use insulin include:
- Syringe magnifier. While this is still utilizing a needle and syringe, it can make the process a lot easier for those with poor vision. A magnifier keeps the needle pen steady, allowing you to clearly see where and when to inject.
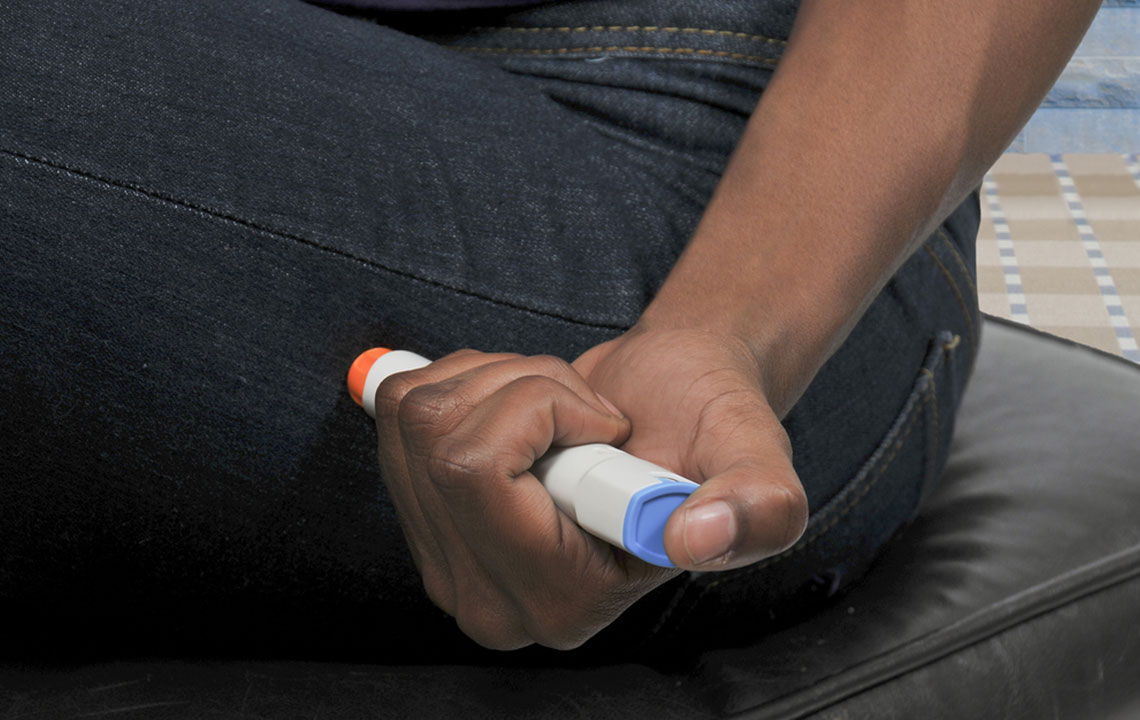
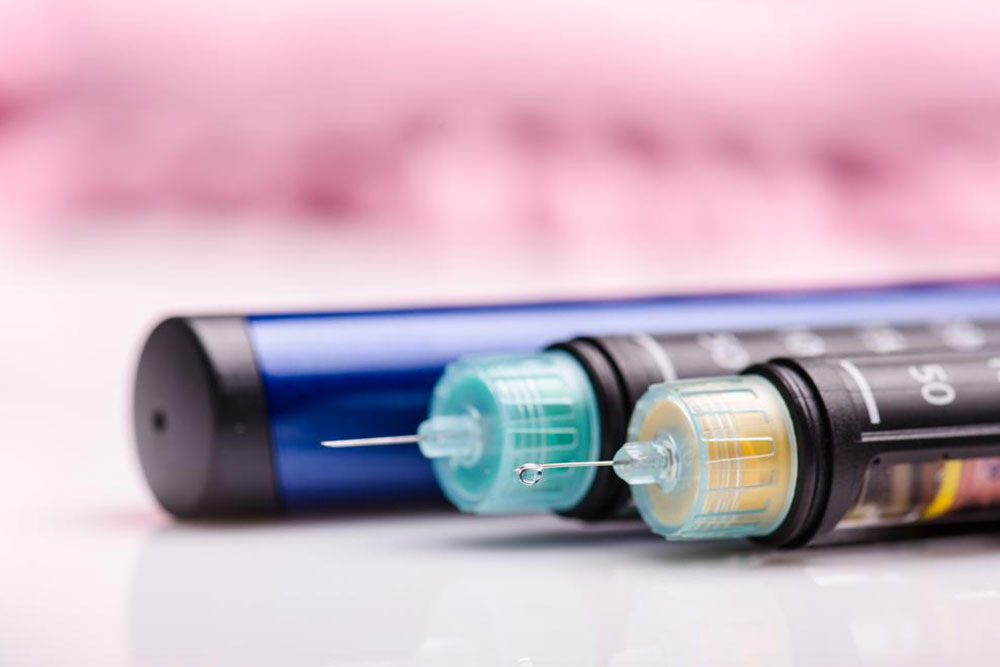
- Insulin pen. These insulin pens are becoming increasingly popular, as they function similar to EpiPens and dispenses insulin straight from the needle. It comes with a cartridge that is already filled with the medication. All you need to do is press the plunger and inject it into your body.
- Insulin pump. The insulin pump is another popular way to inject insulin, it is mainly used by those with vision and other health problems. The pump automatically delivers insulin to your body as it is constantly attached to you. There is a small catheter on the other end of the pump, which is typically inserted into your skin at the abdomen. The small monitor can be programmed to deliver insulin at any time, and at any dose. This handy pump is great for those who need to manage themselves strictly, or in case of an emergency.
- Injection pump patch. The injection pump patch is one of the less invasive ways to deliver insulin to your body. It is a fairly new invention that attaches directly to the skin and pumps insulin directly inside you. It doesn’t use any syringes or tubes to inject with.
No matter your preferred method of insulin use, it is important to find a method that works best for you. These different insulin injection tools can help you maintain your insulin intake on a strict schedule, allowing you to have control over your disease without worry or stress.