Symptoms And Causes Of Deep Vein Thrombosis
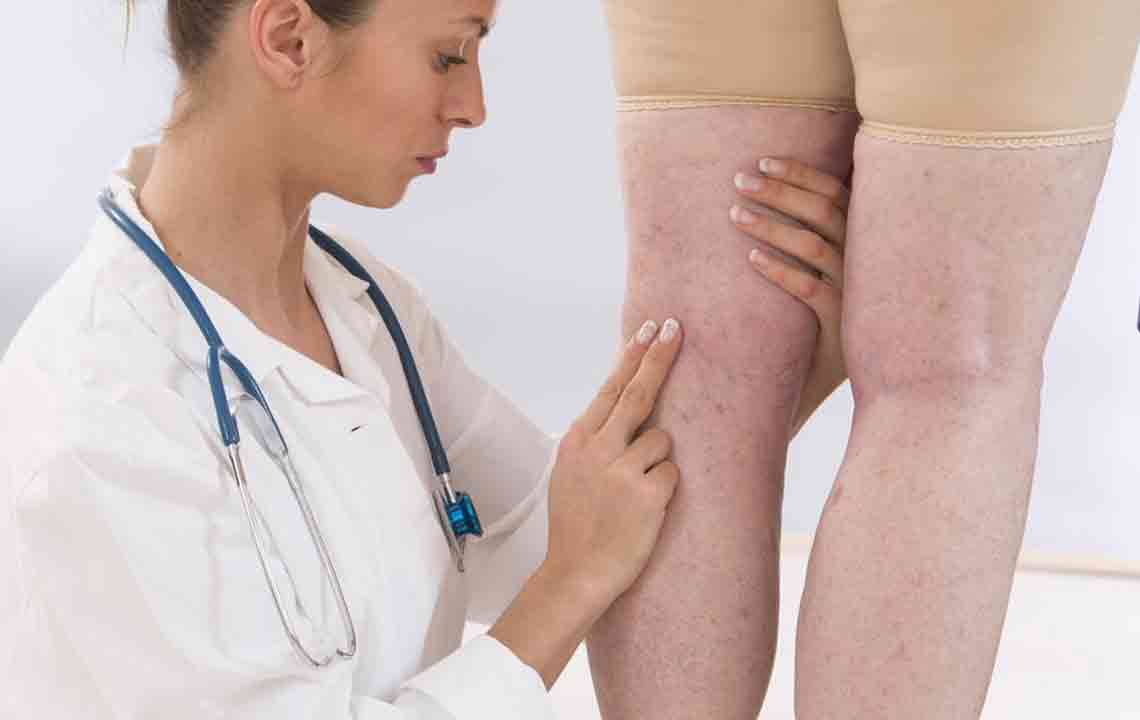
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot forms in the veins. In DVT, the clot forms in one of the deeper veins, and it occurs in one’s legs. DVT can cause pain and cramps in the leg, but it could also lead to a life-threatening condition called Pulmonary Embolism (PE).
Blood clots can occur for various reasons – injury, certain medical conditions, surgery, etc. The risk factors for Deep Vein Thrombosis are:
- A Family History of DVT : If other members of one’s family have been affected by DVT or Pulmonary Embolism, one is at risk for getting this disease.
- Being Overweight : One’s weight exerts more pressure on the veins in the legs and the pelvis. This increases the chances of a blood clot forming in one’s veins.
- Injury : Certain injuries like a fracture that causes damage to the veins, can also raise the chances of developing a blood clot.
- Surgery : Surgery, especially leg surgery like a joint replacement procedure, can lead to the formation of blood clots in some patients.
- Pregnancy : When one is pregnant, the uterus expands, and this affects the normal speed of blood flow. Slow circulation can be a risk factor for the formation of blood clots.
- Age : If an individual is over 60, the chances for DVT increases, especially if they have another risk factor.
- Heart Failure : A heart that is not functioning properly has problems pumping blood and keeping it circulating normally. So this is also a risk factor for DVT.
- Long Bed Rest or Frequent Travel : If one remains seated for long hours while travelling in a car or plane or were bedridden for a long time due to an illness – these also increase the chances for DVT. When one does not move one’s legs for long, the calf muscles are not exercised properly. Regular leg movements make one’s calf muscles contract, which helps to keep the blood moving. If this doesn’t happen often enough, the affected circulation can cause a blood clot.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Symptoms
We have looked at the possible causes of DVT. However, what is the main Deep Vein Thrombosis symptoms? Early diagnosis can help prevent complications. It is estimated that around 300,000 to 600,000 people are affected by DVT in the United States. Unfortunately, not everyone who has Deep Vein Thrombosis shows any outward Deep Vein Thrombosis symptoms of the condition. Even among those who display any Deep Vein Thrombosis symptoms, these signs can be mistaken for normal leg pain or other medical conditions. The Deep Vein Thrombosis symptoms legs that could indicate a blood clot in one’s veins include:
- Sudden onset of pain in the legs
- Swelling in the leg
- The swelling can affect the ankle, foot, or leg
- Tenderness and warmth in the affected area
- Usually, the symptoms deep vein thrombosis leg show up only in one leg; though sometimes, swelling and pain can occur in both legs
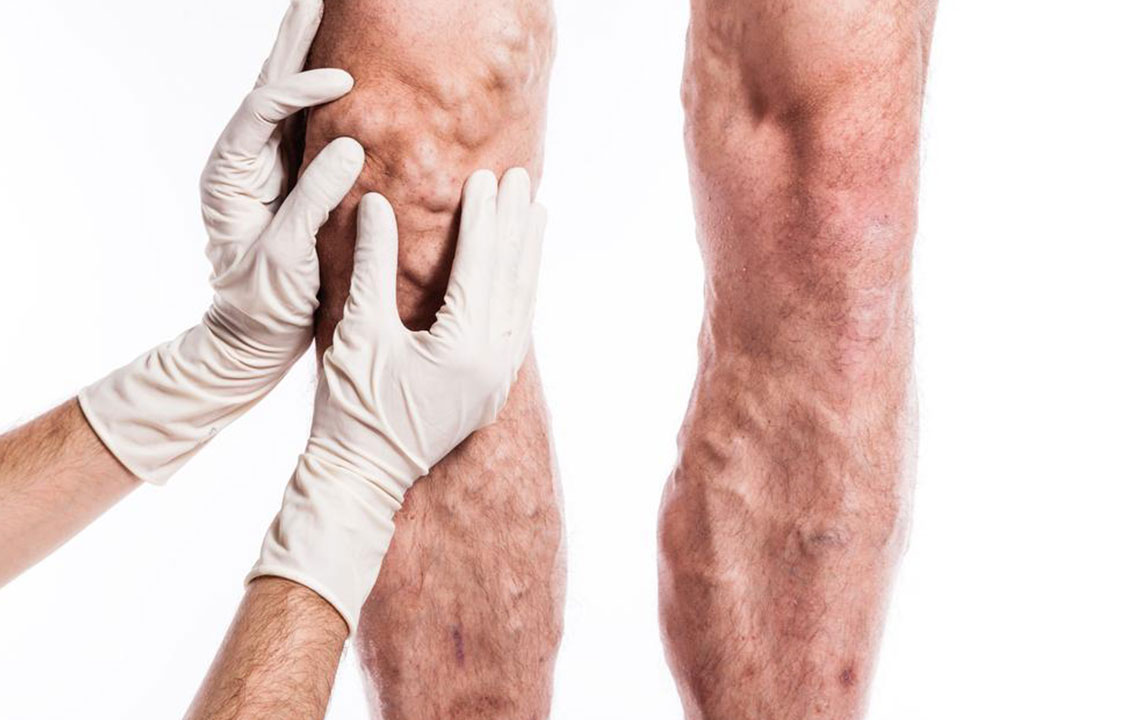
- One can easily observe the veins in the affected region
- Skin in the area can become red or discolored
- Pain, when walking or standing
- Tiredness in the legs
- Cramps in the leg that usually begin in the calf region
In Deep Vein Thrombosis symptoms, legs are the organs which are the most affected. If the pain and swelling persist and even get worse with time, see a doctor. If one ignore these symptoms, or even if one doesn’t show any Deep Vein Thrombosis symptoms, if a blood clot is present in the leg, it could break away and travel up to the lungs, resulting in Pulmonary Embolism. Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism include:
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid breathing
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Severe dizziness
If one experiences these symptoms, it is time to seek immediate medical help.
Diagnosis Procedures
The doctor will study one’s symptoms – Deep Vein Thrombosis. Legs will be examined for signs of the condition, and the doctor may decide to conduct some tests to determine whether the symptoms indicate DVT or some other disorder.
- Ultrasound Test : This is a non-invasive test; one’s leg will be covered with a warm gel, and sound waves would be transmitted over the affected region. This helps form an ultrasound image of the region, letting the doctor see the blood vessels and spot a blood clot. If the blood clot is in the outer or superficial veins, the condition is not serious. If the blood clot is in the inner veins, this test may not always be successful in showing it.
- Venography : This procedure can help highlight a blood clot.
- MRI : Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can be a more reliable way to identify Deep Vein Thrombosis. As one will be lying down on a table that slides into the MRI machine, both legs can be examined at once, and the clear pictures formed can show up any clots in the blood vessels.
If DVT is confirmed, some patients might need surgical procedures to prevent the blood clot from causing Pulmonary Embolism effectively.
The blood clot can disappear and then reappear again. So, if one is diagnosed with DVT or is at risk of the condition, make sure to stay active, lose a few pounds if one is overweight, and exercise the legs to prevent the formation of blood clots.