Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment Of Bowel Problems
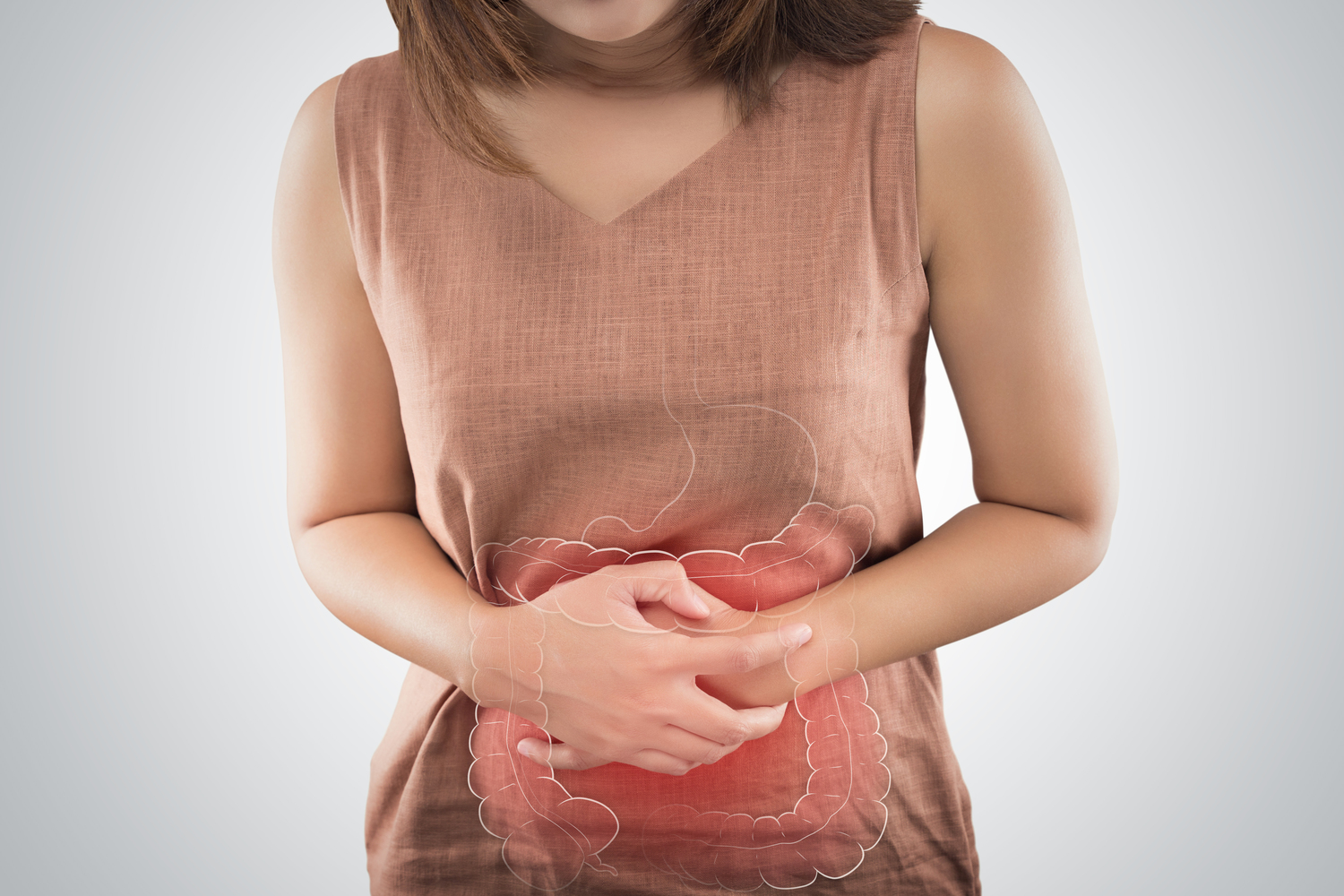
Bowel problems refer to any illness that impacts the gastrointestinal tract. They occur when the movement of food residue and waste products in the intestines is either halted by some kind of bowel obstruction or impacted by the presence of an infection in the body. The smooth movement of bowels heavily determines our overall health and well-being. Remember, anyone may face bowel problems; age is no criteria.
Types of bowel problems
- Constipation :

Common symptoms of bowel problems
- Constipation symptoms include passing fewer than three stools a week, having a feeling of a blockage in the rectum, passing hard or lumpy stools, and straining to pass stools.
- Diarrhea symptoms include the frequent passing of loose and watery stools, abdominal cramps and pain, nausea and vomiting. In severe cases, diarrhea is accompanied by fever, blood, and pus in the stools, and an inability to consume fluids.
- Bowel obstruction symptoms include a mix of constipation and diarrhea, feeling full after consuming little food, nausea and vomiting, heartburn, and a complete absence of flatulence.
Possible causes of bowel problems
Constipation is commonly caused because of the following:
- A side effect of certain medications
- Hypothyroidism
- A lack of fiber in the diet
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Dehydration.
Diarrhea is caused by one of the following reasons:
- A side effect of medications
- Inflammatory bowel diseases
- Consuming excess laxatives to treat constipation
- Food intolerances due to allergies
- High-stress levels
- Infections
Bowel obstruction is common in patients suffering a terminal illness. For instance, cancer as a tumor could be obstructing the movement of the bowels. Bowel obstruction may also occur as a side effect of certain medicines and in people suffering from diseases such as a hernia.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Any traces of blood in the stools
- Severe pain while passing stools
- A change in regular bowel habits which either cause loose motions several times a day or lead to bowel movements less than thrice a week.
- Sudden weight loss accompanied by feelings of tiredness
- Bowel problems accompanied by fever
Treatment options for bowel problems
Treatment varies depending on the type of bowel disorder.
- For diarrhea, the doctor will prescribe antidiarrheal medicines and, in some cases, antibiotics.
- For constipation, the doctor may prescribe stool softeners and painkillers if the cramps are too severe.
- In certain cases, surgery may be advised to remove an intestinal blockage.
- The doctor may also recommend certain tests if bowel problems do not go away on their own. These tests will help determine any underlying disease that might be causing bowel disorders.
Precautions to avoid bowel problems
- Depending on the nature of bowel problems, the doctor may advise changes in diet that involve including more fiber and cutting down on gluten and dairy products.
- Drink lots of water to keep the gastrointestinal tract healthy.
- Exercise regularly to stay fit and keep your muscles active.