Types and Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a severe skin condition that often persists from childhood. One of the most distressing symptoms is intense itching of the skin, which can significantly affect one’s quality of life. While there is no definitive cure for atopic dermatitis, there are effective ways to manage the condition and alleviate its symptoms. But it’s imperative to learn about the key signs of AD for early identification and proper management.
Types of atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is considered the most common yet severe form of eczema, a skin condition that causes rashes and inflammation. It is further categorized into two types, intrinsic and extrinsic, based on the levels of Immunoglobulin E (or IgE), an important type of antibody in the immune system.
- Intrinsic
Non-allergic atopic dermatitis, also called intrinsic dermatitis, is more common in children. In this type of atopic dermatitis, the level of Immunoglobulin E (or IgE) in the body is normal. - Extrinsic
Allergic atopic dermatitis, also referred to as extrinsic dermatitis, is more frequently seen in adults. The key factor that differentiates extrinsic AD from intrinsic AD is the higher level of immunoglobulin E in the body. Elevated IgE levels indicate that the body is reacting excessively to allergens.
Signs of atopic dermatitis
This skin condition exhibits certain signs and symptoms that are easily noticeable during flare-ups.
Itchy skin
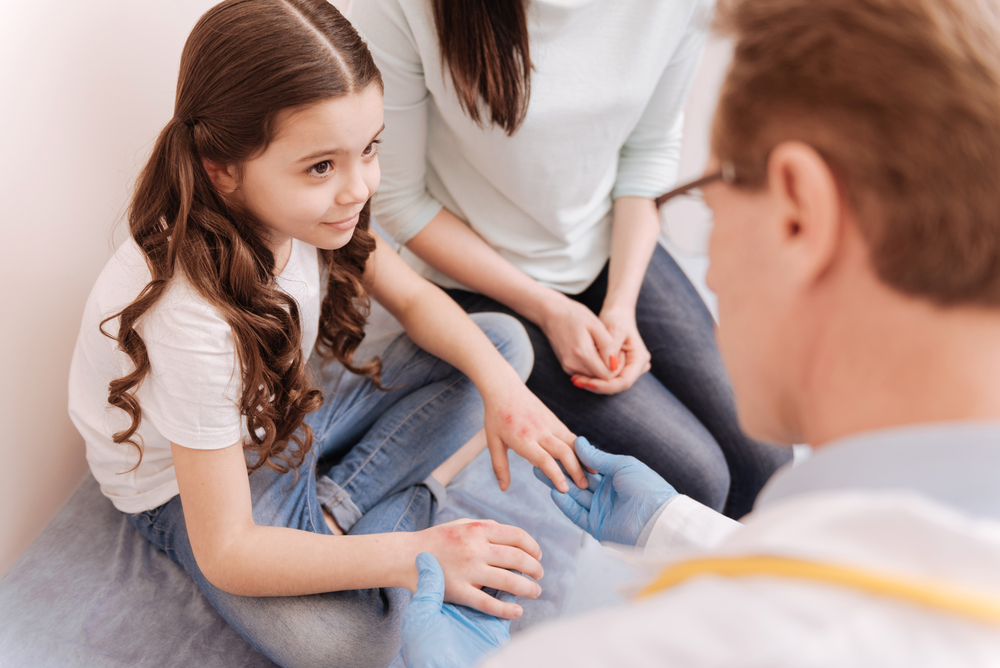
One of the most common signs of atopic dermatitis is chronic and persistent skin itching, known as pruritus. The itching can also have occasional flare-ups with periods of improvement in between. In severe cases, this sign can be so intense that one may find it difficult to resist the urge to scratch, sometimes leading to bleeding and inflamed skin. It is important to note that AD can cause this symptom in both adults and infants.
Dry skin
With the onset of AD, affected individuals may also notice extreme dryness and cracking of the skin, which can worsen irritation and overall discomfort. Dry skin is often observed on the face and scalp of infants, while adults and older children typically experience the symptoms on their elbows, knees, wrists, ankles, and neck.
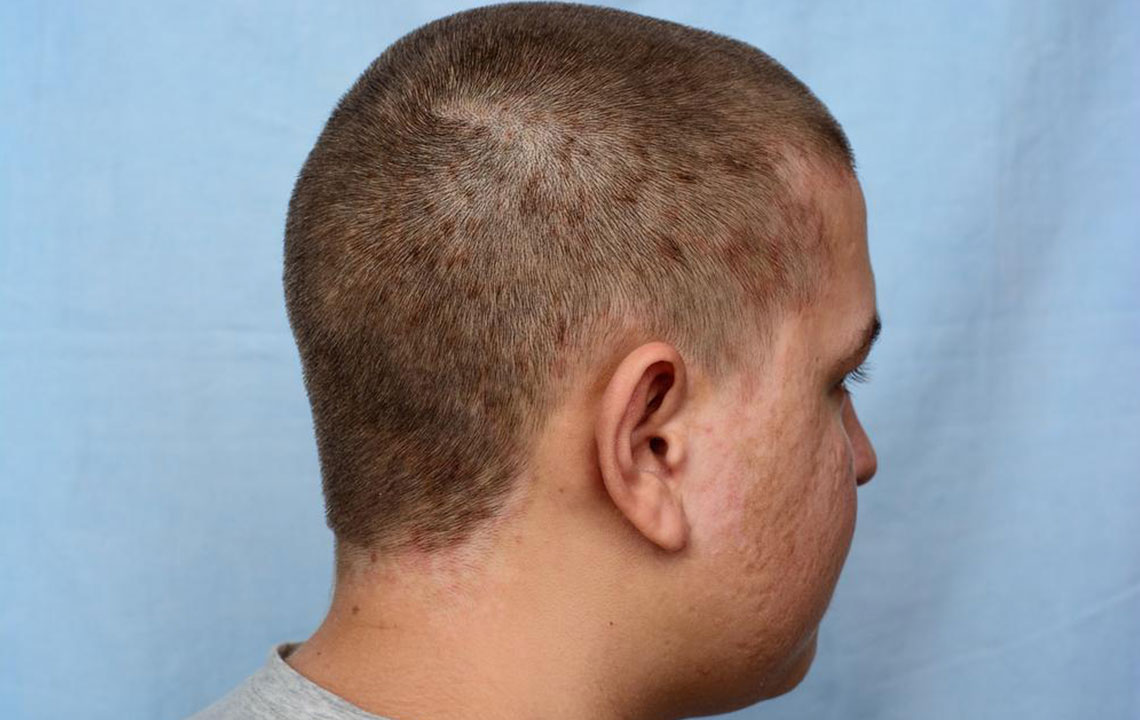
Rashes
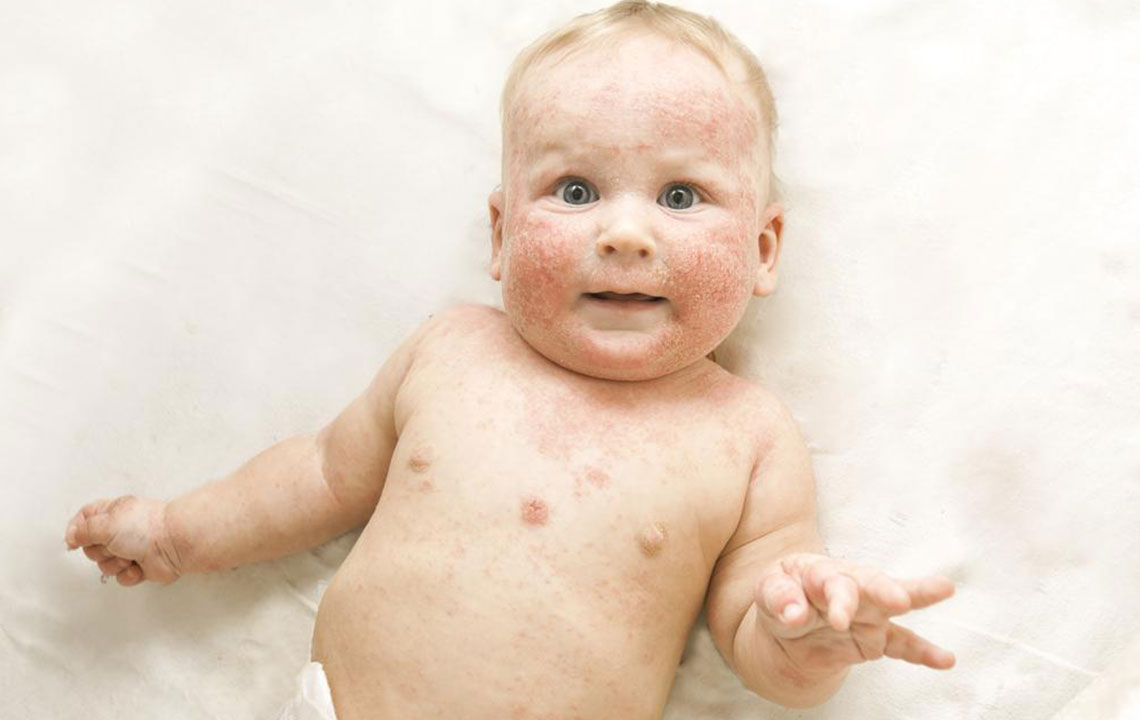
Red, purple, or brownish-grey rashes can begin to develop anywhere on the body. But, in adults, rashes due to AD most commonly appear on knee folds or elbow joints, on the back of the hands, or the scalp. As kids grow, they can develop rashes in areas similar to those of adults. In some cases, children may also experience rashes on their neck and face. On the other hand, infants typically get rashes only on their scalp or cheeks.
In many cases, rashes forming due to atopic dermatitis can leak and ooze fluid. This sign can be noticed in both infants and adults.
Inflamed skin
Atopic dermatitis can also cause the skin to appear swollen due to inflammation. This inflammation is not contagious and can affect both infants and adults. Affected individuals may also experience inflammation around the lips and eyelids due to this condition. The inflamed areas of the skin may also feel warm to the touch.
Small bumps on the face (in infants)
A common sign of atopic dermatitis in infants is the formation of small bumps on their faces. These bumps often occur on their cheeks and scalp.
Thickened patches of skin
As the condition progresses, the affected areas of the skin permanently thicken and develop a leathery texture. This sign is called lichenification, which is most commonly noticed in long-term atopic dermatitis. Sometimes, one may also notice their skin thickening due to constant itching and scratching.
An increase in skin infections
Affected individuals are at a higher risk of incurring skin infections. The primary reason for this is constant scratching and itching, which weakens the upper layer of the skin. Due to skin infections, one may also begin noticing signs such as pustular discharge from the inflamed area, the affected patch of skin becoming red, and the area feeling painful and warm to the touch.
Difficulty staying asleep
In some cases, the itching can become so persistent and bothersome that it affects one’s sleep quality. The itchiness may suddenly flare up in the middle of the night, interrupting one’s sleep, or it may be so intense that it can keep one from falling asleep at all.
Irritability
Constant itching and inflamed skin can cause the affected person to feel extremely irritable, especially if the condition has been affecting one’s sleep cycle. Several other aspects of atopic dermatitis, such as rashes, pain, and periodic flare-ups, can also make one anxious and irritable, severely affecting one’s quality of life. One might also feel embarrassed about participating in a social gathering.
Consult a dermatologist as soon as possible if one experiences any signs related to the condition. Those unsure about the condition’s physical symptoms can do a simple online search with relevant keywords like “what an atopic dermatitis rash looks like.”